Distally the linea aspera forms two ridges known as. Any of several prominences on the distal part of a long bone serving for the attachment of muscles and ligaments.
Orif Lag Screw For Lateral Medial Femoral Epicondyle Fracture
Medial Epicondyle Anatomy - 13 images - open reduction and internal fixation of fractures of the medial epicondyle musculoskeletal key anconeus epitrochlearis muscle anatomy medical education medicine orthopedic surgery orthopedics normal radiographic anatomy of the knee radiology case anatomy of the knee individual muscles of forearm flexors of digits.

. Femur - largest long bone Medial lateral epicondyles Tibia Medial malleolus - medial ankle Fibula Lateral malleolus - lateral ankle Investing Fascia Fascia lata - envelopes thigh Iliotibial tract - lateral thickening attached to lat. The linea aspera then diverges toward the distal third of the femur where the medial and lateral lips become continuous with their respective ipsilateral supracondylar line medial and. One on the outer aspect of the distal part of the humerus or proximal to the lateral condyle of the femur.
Medical Definition of epicondyle. Under fluoroscopy the superior medial and lateral epicondyles of the femur as well as the distal aspect of the medial tibial epicondyle of the affected knee were identified as the target zones for the injections using an AP view. The thigh bone is called the Femur.
The medial epicondyle is the larger. Tibial condyle Saphenous opening - for greater saphenous v. There are two condyles found on the proximal end of the tibia and those are known as the medial and lateral condyles of tibia.
This tendinous part here forms an intermuscular septum which forms. Know the Head of the Femur and that it attaches to the hip joint called the Acetabulum. On the medial side it is within the flexor carpi radialis and pronator teres origin.
The medial and lateral condyles are found on the distal end of the femur and those articulate with the knee joint. Lateral Medial Epicondyles. The Femur has a Greater Lessor Trochanter.
The medial and lateral lips unite along the middle third of the femoral shaft traveling medial to the nutrient foramen. Directly below it is a small depression from which a smooth well-marked groove curves obliquely upward and backward to the posterior extremity of the condyle. The histology of epicondylitis has been described as angiofibroblastic hyperplasia.
The intercondylar fossa of the femur is located between the lateral and medial epicondyles of the femur between the greater and lesser trochanter of the femur between the lateral and medial condyles of the femur between the lateral and medial condyles of the humerus between the lateral and medial. Namely the presence of fibroblasts and vascular tissue along with. The femoral attachment point taking the anterior-posterior medial femoral condyle diameter to be 100 was identified 40 from the posterior 50 from the distal and 60 from the anterior border of the medial femoral condyle.
What muscles attach to the medial epicondyle knee. Medial and lateral epicondyles ofthe femur 4. Bones and area to remember.
Directly below it is a small depression from which a smooth well-marked groove curves obliquely upward and backward to the posterior extremity of the condyle. N544 TG3-02 Femoral n. Medial epicondylar avulsion fractures are the most common avulsion injury of the elbow and are typically seen in children and adolescents 4.
The medial epicondyle is anterior to the lateral epicondyle. Each region was marked and the overly skin and subcutaneous tissues were infiltrated with a total of 3 mls of 1. It also contains both medial and lateral condyles.
Located above the medial condyle it bears an elevation the adductor tubercle which serves for the attachment of the superficial part or tendinous insertion of the adductor magnus. Adductor tubercle Patella N507TG3-06TG3-56 N511. Which bone does not.
Medial lateral epicondyles Pectineal line of femur. Lateral femoral cutaneous n. Styloid process of the fibula 14 Head and base of metatarsals Medial and lateral condyles of the femur.
Apex of the patella b. Directly below it is a small depression from which a smooth well-marked groove curves obliquely upward and backward to the posterior extr. Tibia refers to the shin bone.
Crural fascia - leg fascia. On the lateral side the primary focus of damage is within the extensor carpi radialis brevis. The bump on the outer side of the elbow is called the lateral epicondyle.
The pelvis is overrotated and the femoral epicondyles are not aligned perpendicular to the imaging table. Lateral condyle is broader than medial condyle of the femur. This point was most isometric with a mean maximal length change to the central patellar attachment of 21 mm.
The structure indicated is the lateral femoral condyleThe distal end of the femur forms two rounded condyles which articulate with the tibia below and the patella anteriorly the medial condyle and the lateral condyleThe linea aspera is a roughened crest of bone on the posterior aspect of the femur. Medial and lateral epicondyles bony elevations on the non-articular areas of the condyles. Medial epicondyle fractures are often associated with elbow dislocation and make up approximately.
The lateral epicondyle of the femur smaller and less prominent than the medial epicondyle gives attachment to the fibular collateral ligament of the knee-joint. Anatomy and Physiology questions and answers. On the femur two types of condyles occur in the knee joint.
Femur Pelvic Bone Connection. The medial epicondyle of the femur is an epicondyle a bony protrusion located on the medial side of the femur at its distal end. The lateral epicondyle of the femur smaller and less prominent than the medial epicondyle gives attachment to the fibular collateral ligament of the knee-joint.
N500 TG3-17 N540 TG3-63 Anterior femoral cutaneous nn. The medial condyle is larger than the lateral outer condyle due to more weight bearing caused by the centre of mass being medial to the knee. The greater trochanter is demonstrated laterally and the lesser trochanter is obscured.
Intercondylar fossa a deep notch on the posterior surface of the femur between the two condyles. The medial epicondyle of the femur is an epicondyle a bony protrusion located on the medial side of the femur at its distal end. The medial and lateral condyles of the tibia articulate with the a.
The medial and lateral collateral ligaments of the knee originate from their respective epicondyles. ㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡ Apex ofthe patella 6. The medial condyle is one of the two projections on the lower extremity of femur the other being the lateral condyle.
Medial and lateral epicondyles of the femur d. Head of the fibula e. Medial and lateral condyles of the femur c.
Greater and lesser trochanters of the femur. The lateral epicondyle of the femur smaller and less prominent than the medial epicondyle gives attachment to the fibular collateral ligament of the knee-joint. The medial and lateral condyle of the tibia are shown in figure 1.
Medial and lateral condyle. The bony prominences or bumps at the bottom of the humerus are called the epicondyles. Medial condyle is much larger and bears more weight.
7Tibial tuberosity 8Tibial spine 9 Ubial plateau 10Medial and lateral condyles of the tibia 11.

Bones Specialist Knee Surgeon In Manchester Professor Sanjiv Jari
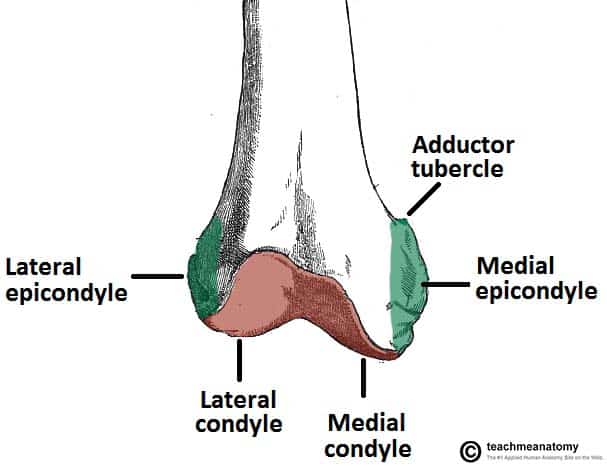
The Femur Proximal Distal Shaft Teachmeanatomy

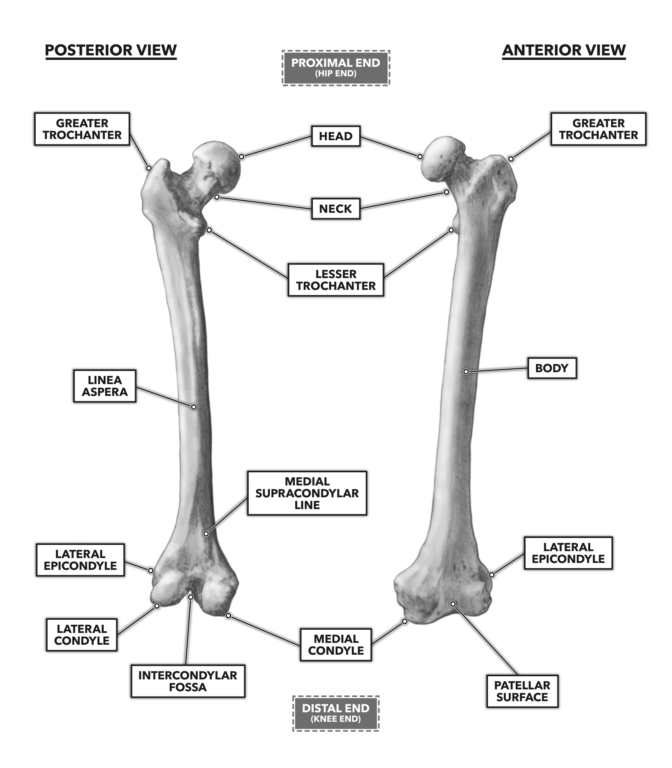
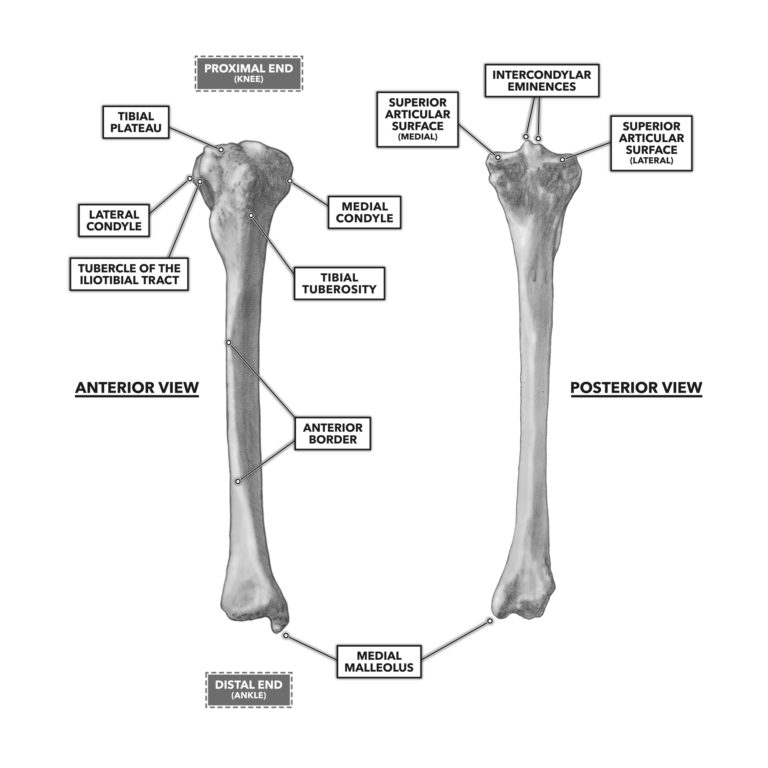


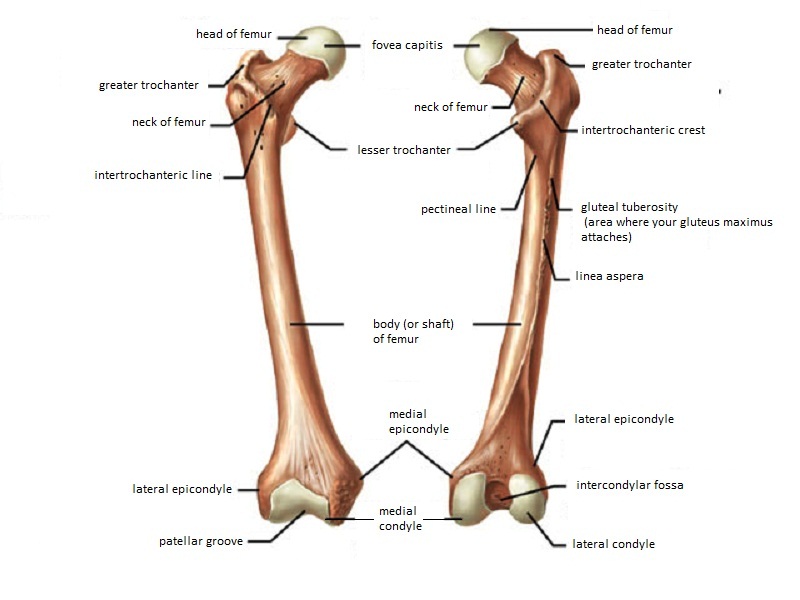
0 comments
Post a Comment